Humberto is a name that has appeared multiple times during past Atlantic hurricane seasons. In 2025, Tropical Storm Humberto will once again become one of the seasons named storms, with the potential to become Hurricane Humberto if it strengthens.
In this article, we’ll look back at the history of storms named Humberto, where they formed, how strong they became, and the impact they had. It also includes practical tips to help with hurricane preparation as the season continues.
Humberto Over the Decades
1995 Hurricane Humberto
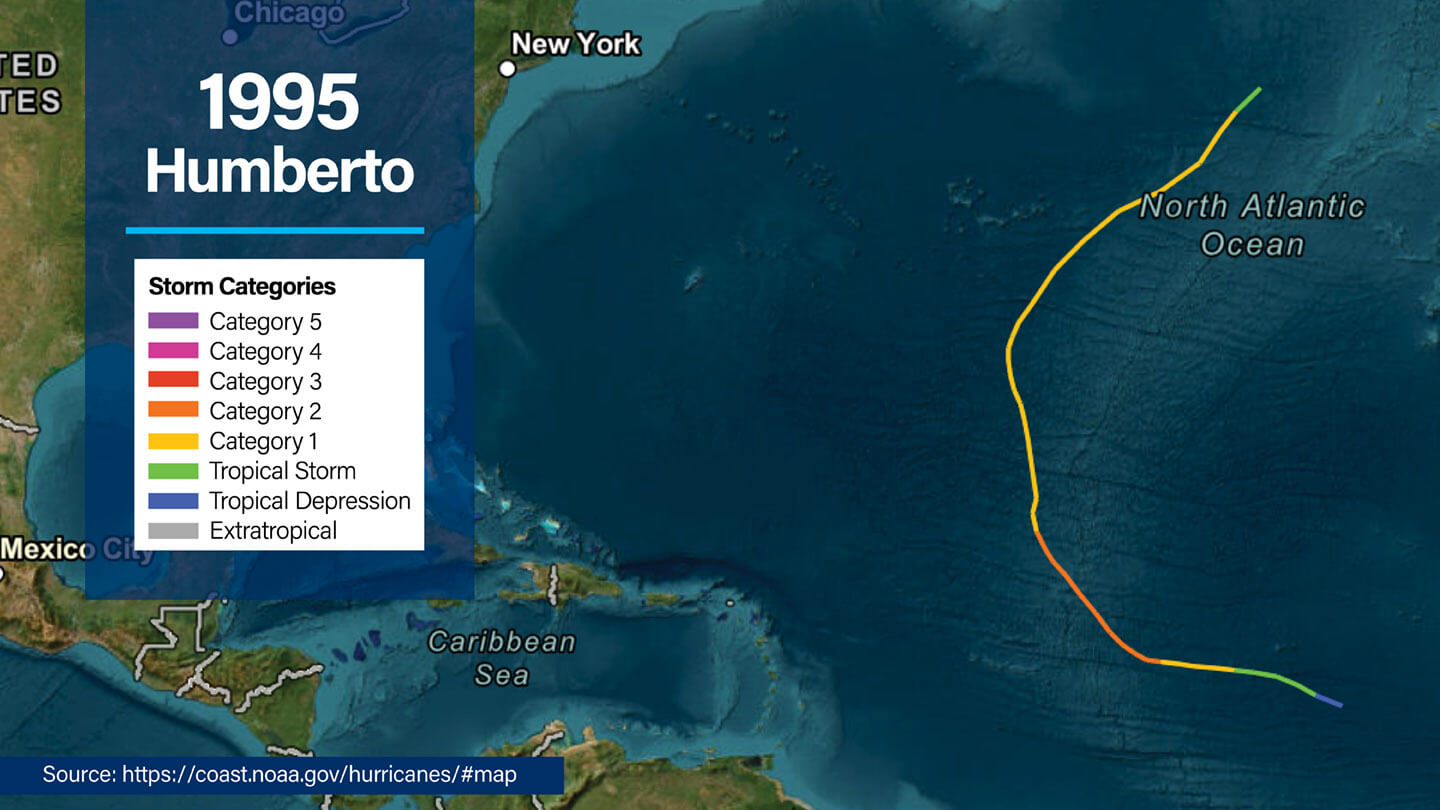
- Dates active: August 22 to September 1
- Peak intensity: Category 2, 110 mph winds (95 knots), central pressure of 968 millibars (mb)
- This hurricane traveled across the open Atlantic without affecting land. It intensified rapidly after forming near Africa, under conditions of warm waters and low wind shear.
- Coexistence with four other cyclones (Iris, Jerry, Karen, Luis) added complexity to meteorological monitoring.
2001 Hurricane Humberto
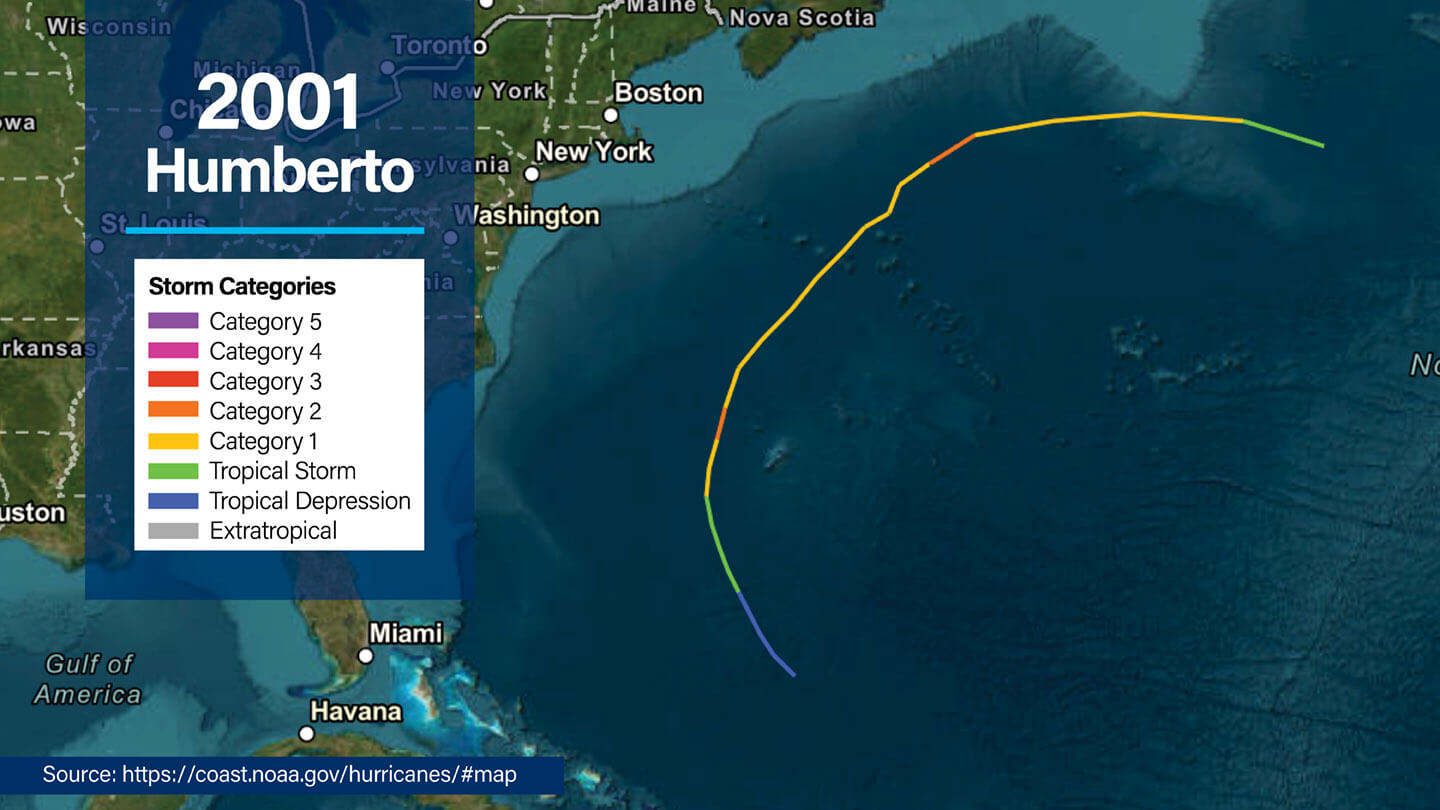
- Dates active: September 21 to 27
- Peak intensity: Category 2, 103 mph winds (90 knots), central pressure of 970 mb
- Passed near Bermuda, causing wind gusts up to 42 mph (37 knots) but with minimal damage or rain accumulation.
- Shear and environmental interaction limited its intensification near subtropical waters.
2007 Hurricane Humberto
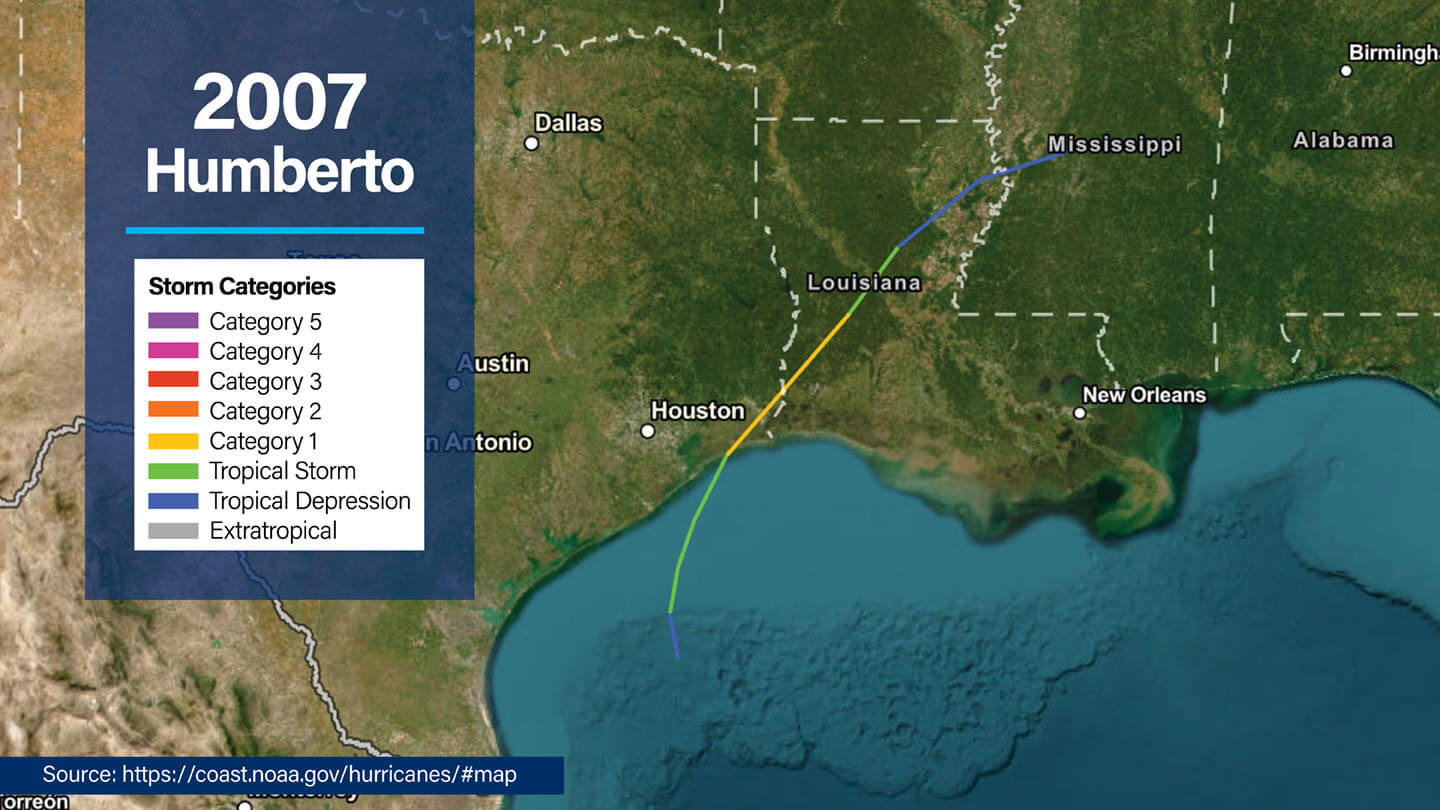
- Dates active: September 12 to 14
- Peak intensity: Category 1, 92 mph winds (80 knots), central pressure of 985 mb
- Humberto made landfall east of High Island, Texas, notable for intensifying from a depression into a hurricane in just 19 hours.
- Impacts included heavy rainfall (over 14 inches in parts of Texas) and localized flooding with a narrow zone of hurricane-force winds.
2013 Hurricane Humberto
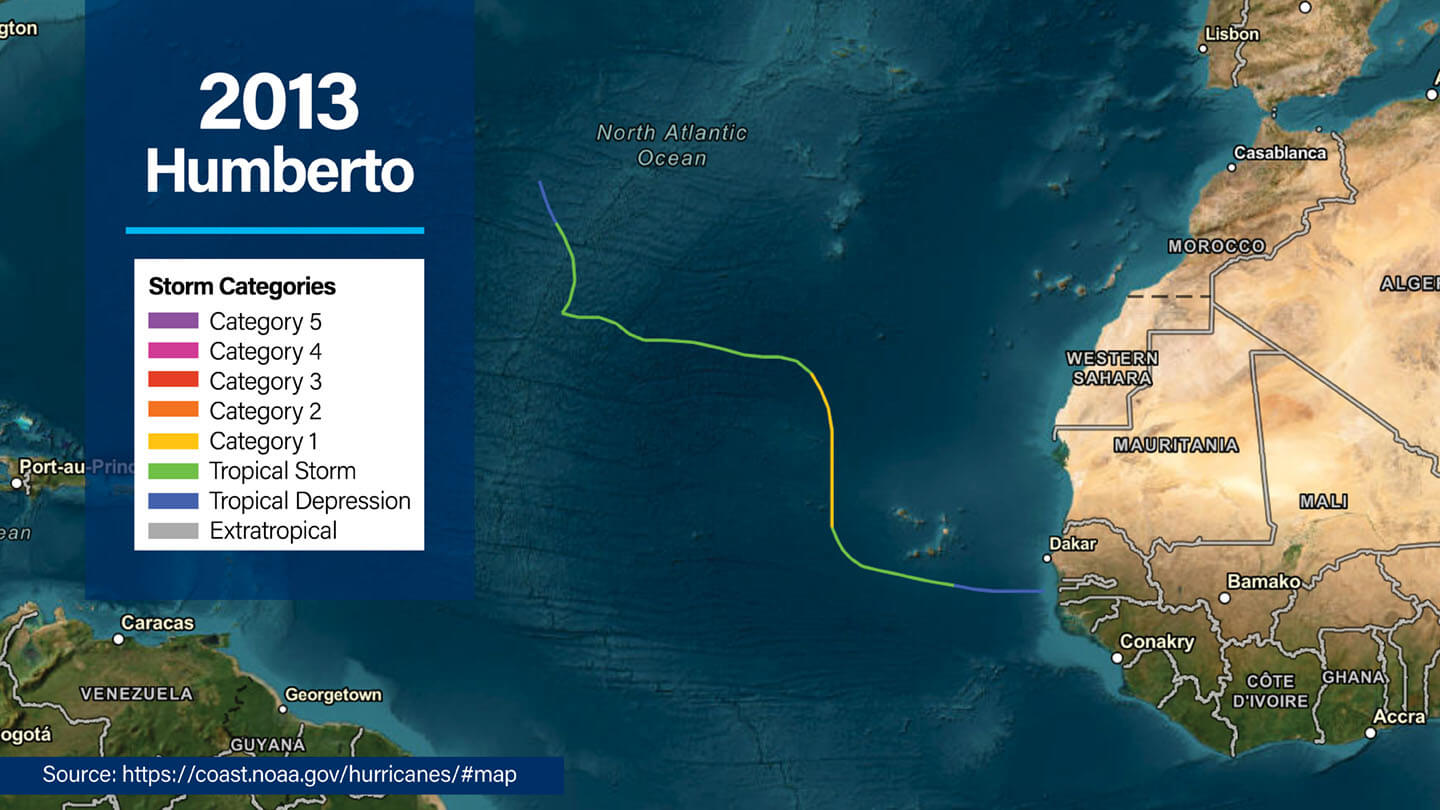
- Dates active: September 8 to 19
- Peak intensity: Category 1, 92 mph winds (80 knots), central pressure of 986 mb
- Humberto brought strong winds and heavy rain to Cape Verde before turning northeast and weakening.
- Marked by a weakening, redeveloping pattern due to shear despite attempts at restrengthening in the central Atlantic.
2019 Hurricane Humberto
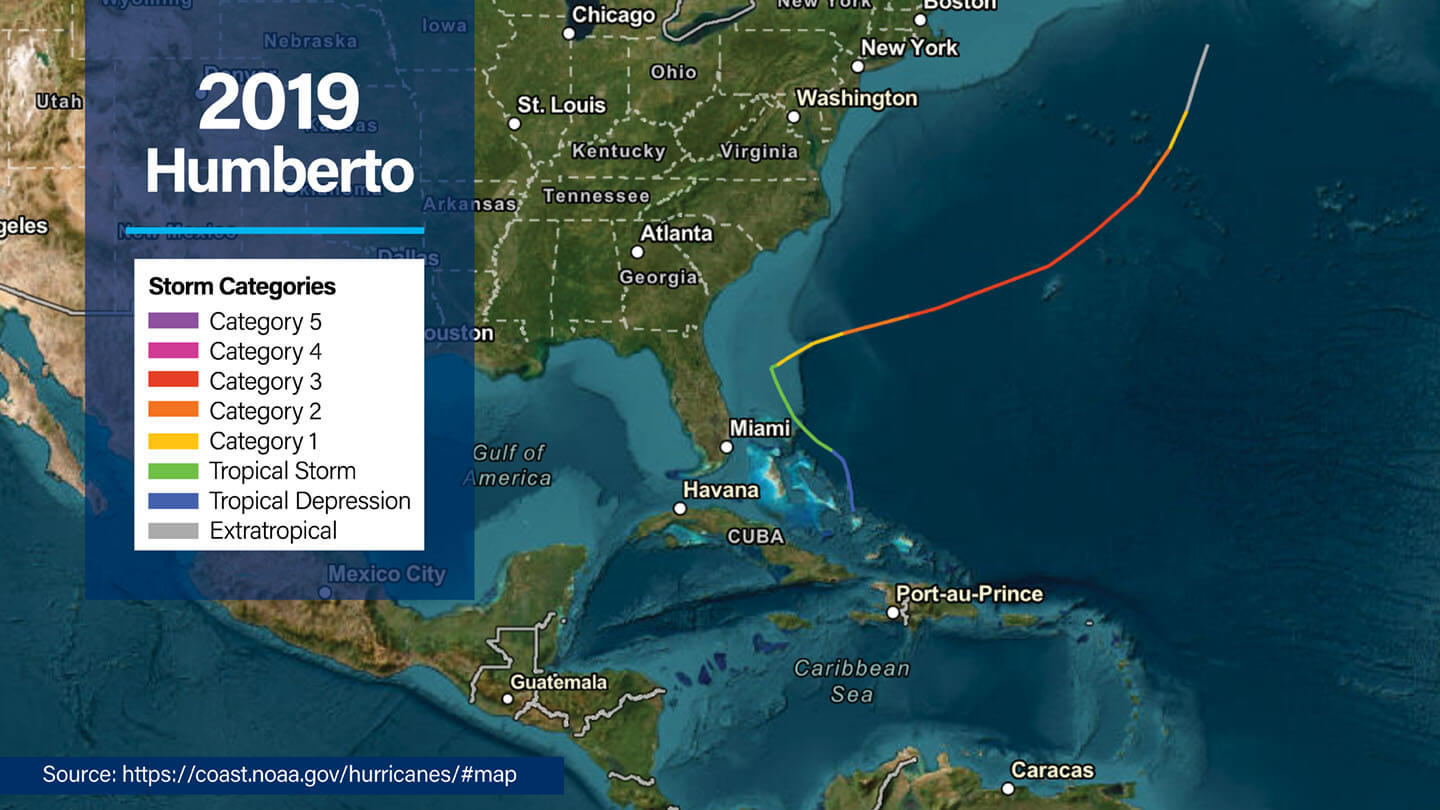
- Dates active: September 13 to 19
- Peak intensity: Category 3, 126 mph winds (110 knots), central pressure of 950 mb
- This major hurricane impacted Bermuda directly, causing extensive wind damage with gusts up to 143 mph (125 knots) and moderate storm surges of about 3 feet along west-facing shores.
- Humberto became extratropical after passing Bermuda and was absorbed by a larger system shortly after.
Key Characteristics of Humberto Storms
Common themes have emerged across the seasons involving Humberto, shedding light on tropical cyclone behavior:
Rapid Intensification
Both 2007 and 2019’s Humberto storms exhibited rapid intensification. This process can transform a tropical storm into a hurricane within hours, increasing unpredictability and risks to coastal regions. This year, Tropical Storm Gabrielle rapidly intensified into Hurricane Gabrielle, making a similar scenario for Humberto more likely. The National Hurricane Center (NHC) has already noted “The storm is within a favorable environment for strengthening…“
Isolated Pathways
Excluding the storms in 2007 and 2019, many of Humberto’s iterations avoided landfall entirely, developing and dissipating over open water. It remains to be seen what path 2025 Tropical Storm Humberto will follow.
Limited Geographical Impact
Although Humberto has affected areas such as Bermuda and parts of the Gulf Coast, its impacts have typically been localized rather than widespread. Meteorologists are keeping a close eye on 2025 Tropical Storm Humberto to see whether it will heavily affect populated communities or have a lighter impact.
Meteorological Highlights and Patterns
Across its iterations, Humberto has demonstrated a variety of behaviors:
- Quick Strengthening: The 2007 Humberto strengthened astonishingly quickly, reaching hurricane intensity barely before landfall.
- Cape Verde Influence: The 1995, 2013, and 2019 storms originated near the Cape Verde Islands, a region known for producing powerful Atlantic hurricanes.
- Diverse Tracks: While some Humberto storms remained over water, others significantly impacted coastal areas, particularly Bermuda and southeastern Texas.
Key Figures Across Humberto Storms
| Year | Peak Winds | Pressure | Observations |
| 1995 | 109 mph (95 knots) | 968 mb | Stayed over open Atlantic with no land impacts |
| 2001 | 104 mph (90 knots) | 970 mb | Passed near Bermuda; brought some wind and rain, but no major damage |
| 2007 | 92 mph (80 knots) | 985 mb | Made landfall in Texas; caused heavy rainfall and localized flooding |
| 2013 | 92 mph (80 knots) | 986 mb | Formed near Cape Verde; remained weak and short-lived with minimal impact |
| 2019 | 127 mph (110 knots) | 950 mb | Tracked close to Bermuda; caused widespread power outages and coastal damage |
Understanding Impacts from Humberto Storms
Localized Flooding Risks
Coastal and inland flooding risks were prevalent in both the 2007 Texas landfalls and Bermuda’s rain-soaked aftermath in 2019.
Flood-prone areas can mitigate future risks by cross-referencing rainfall analytics from Humberto 2007’s 14-inch record rainfall assessments.
Infrastructure Damages (Post-Landfall)
2007 Hurricane Humberto caused localized damage in southeastern Texas and southwestern Louisiana. The storm left 120,000 homes in Texas and 13,000 in Louisiana without power.
Total damage was around $50 million, with most caused by flooding, strong winds, and downed trees. The impact was limited due to the storm’s small size and the region’s prior experience with Hurricane Rita in 2005.
Accurately forecasting storms like Humberto is critical for understanding their impact. For organizations tracking seasonal weather patterns, studying spaghetti hurricane data models can help with more accurate forecasting.
Preparing for Future Storms Named Humberto
Understand the Storm Cycle
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO), responsible for naming storms, maintains six lists recycled every six years. Names are retired if a storm causes extreme destruction. Humberto is still on the list due to relatively moderate impacts across its history.
Hurricane Season Insights
Hurricanes like Humberto usually form between June and November, peaking during late August and September. For an in-depth look at hurricane season in the U.S., check out our articles discussing hurricane season in Texas and Florida.
Boosting Preparedness
Whether expecting minor impacts or a Category 3 hurricane, preparedness is a must:
- Develop a Communication Plan so your family or organization can stay connected.
- Stock Up on Emergency Supplies for at least three days, including water, non-perishable food, and flashlights.
- Monitor Storm Updates through reputable sources to avoid misinformation.
- Reinforce Your Home by securing loose outdoor items and checking your property’s structural integrity.
Review a comprehensive breakdown of how to prepare with our Developing a Comprehensive Emergency Management Plan article.
Frequently Asked Questions About Humberto
Which Humberto storm has been the strongest?
Humberto in 2019 reached a peak intensity of 125 mph, making it the most powerful storm under this name.
What makes a hurricane like Humberto unpredictable?
Rapid intensification, as seen in 2007, and environmental factors like wind shear and dry air, which influenced 2013, contribute to unpredictability.
Where can I learn more about named storms?
Explore interesting facts about hurricanes and tropical storms on Interesting Facts About Hurricanes for deeper insights.
Staying informed about past storms like Humberto equips us to face future challenges with greater resilience and preparedness.
What makes 2019 Humberto stand out among other hurricanes?
Humberto 2019 demonstrated Bermuda’s vulnerability to Category 3 hurricanes, serving as a case study in the importance of weather-resilient infrastructure.
How does rapid intensification occur in tropical cyclones like Humberto?
Rapid intensification happens when storms encounter warm ocean waters, low wind shear, and ideal atmospheric conditions, enabling quick strengthening.
Why hasn’t Humberto been retired as a storm name?
The name Humberto is still used because its associated storms haven’t caused catastrophic damage or loss of life relative to storms with retired names.
When is the peak time for Humberto-like storms?
Typically, the peak for storms named Humberto falls between late August and September, aligning with the most active part of the Atlantic hurricane season.
What made Hurricane Humberto in 2007 unique?
2007’s Humberto set a record for its rapid development, transitioning from a tropical depression to a hurricane in just 19 hours.
Where did Hurricane Humberto hit in 2007?
Hurricane Humberto in 2007 made landfall in Texas and caused the most damage out of all storms named Humberto, with torrential rains, wind impacts, and one fatality.
How are hurricanes like Humberto monitored?
Storms like Humberto are tracked using satellite imagery, reconnaissance flights, and advanced modeling, predicting path, intensity, and potential impacts.




