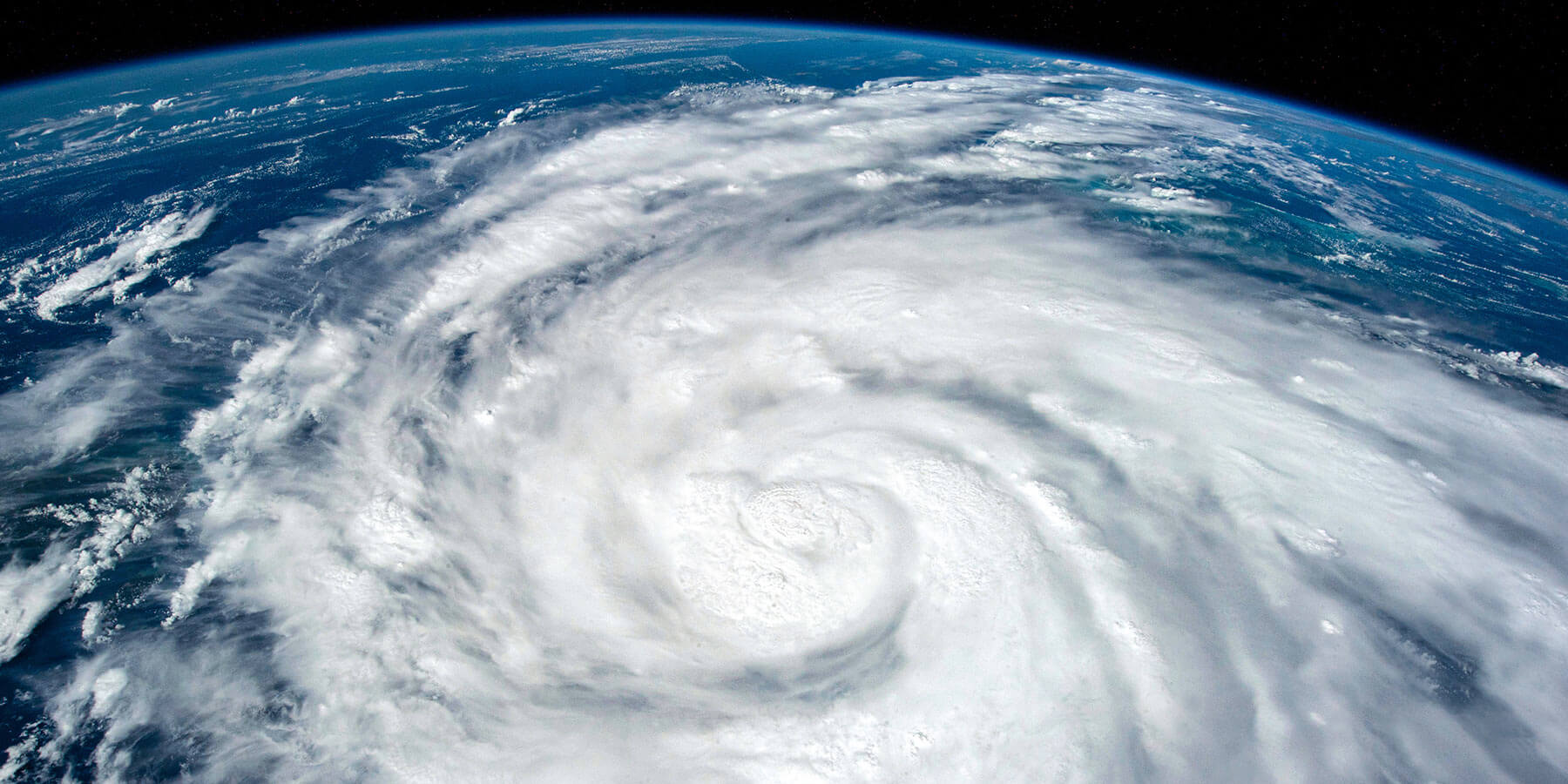
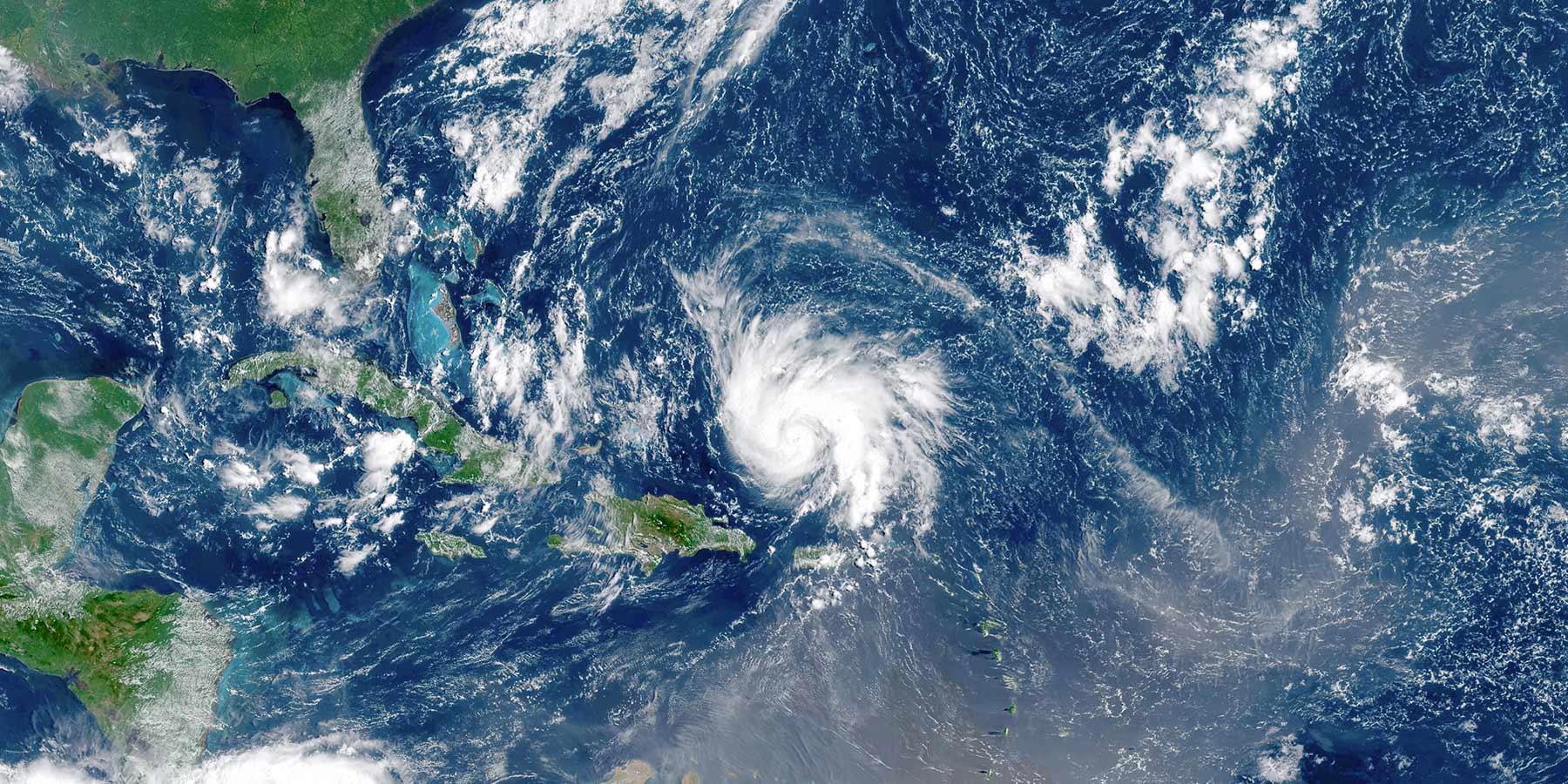
In the heart of the Caribbean, Puerto Rico is a vibrant territory known for its rich culture, beautiful landscapes, and, unfortunately, its susceptibility to hurricanes. While hurricane season in Puerto Rico can be unpredictable, it is a fairly regular phenomenon, and because of that, emergency management and preparedness are always a top priority.
In this article, we’ll explore the nuances of hurricane season in Puerto Rico and the meteorological patterns that influence it.
The Predictability and Impact of Hurricane in Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico’s hurricane season aligns with the broader Atlantic hurricane season, typically spanning from June 1st to November 30th.
Key Data Points
- Historical Impact
Puerto Rico has faced severe hurricanes like Hurricane Okeechobee (1928) and Hurricane San Ciprian (1932), causing widespread devastation. The more recent devastation caused by Hurricanes Irma and Maria in 2017 further underscores the island’s vulnerability to hurricanes. - Frequency
On average, Puerto Rico is affected by a tropical storm or hurricane around 4 times per year.
The Science and Patterns of Hurricanes Affecting Puerto Rico
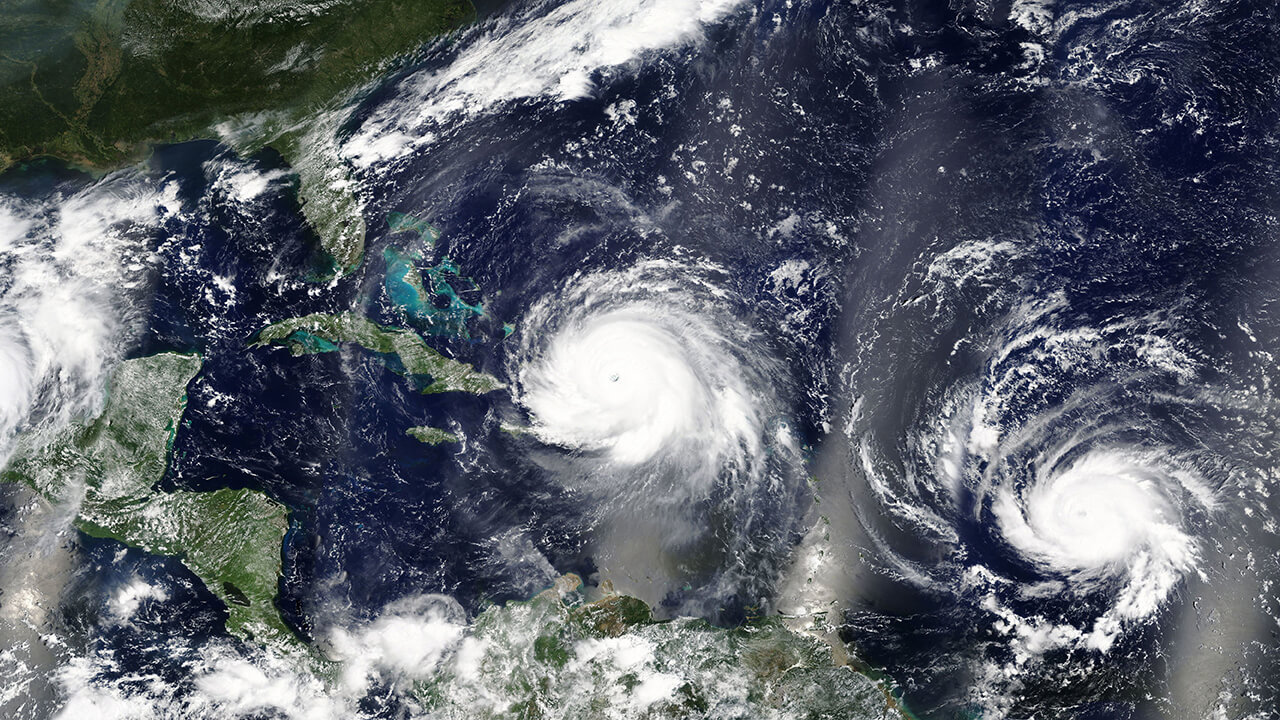

The science behind the formation and trajectory of hurricanes affecting Puerto Rico is a field of study that encompasses meteorology, oceanography, and climatology. The island’s geographical position in the northeastern Caribbean makes it particularly susceptible to the path of hurricanes developing in the Atlantic basin. Here are a few key factors that contribute to this vulnerability.
Sea Surface Temperatures (SSTs)
One of the most critical elements in hurricane formation is warm sea surface temperatures. Hurricanes gain their strength from the heat of the ocean, requiring SSTs of at least 26.5°C (approximately 80°F) to form and sustain themselves. The waters surrounding Puerto Rico, particularly during the peak hurricane months from August to October, often exceed this threshold, providing an ideal environment for hurricane development and intensification.
Atmospheric Conditions
For hurricanes to form and sustain, specific atmospheric conditions must be met. These include a moist lower to middle atmosphere, low wind shear, and pre-existing weather disturbances. The region’s atmospheric conditions during hurricane season often include high humidity levels, which contribute to the formation of thunderstorms—a key component in the development of hurricanes. Additionally, the presence of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) near the region can provide the necessary lift and instability for storm formation.
Prevailing Wind Patterns
The prevailing wind patterns, including the easterly trade winds and the steering currents at higher levels of the atmosphere, play a significant role in the trajectory of hurricanes toward Puerto Rico. These winds generally move from east to west across the Atlantic, guiding storms from their genesis points near the African coast or the eastern Atlantic towards the Caribbean. The position and strength of the Bermuda High, a high-pressure system in the Atlantic, also significantly influence the path and speed of hurricanes, often directing them toward the Caribbean and, by extension, Puerto Rico.
Puerto Rico’s Geographical Location
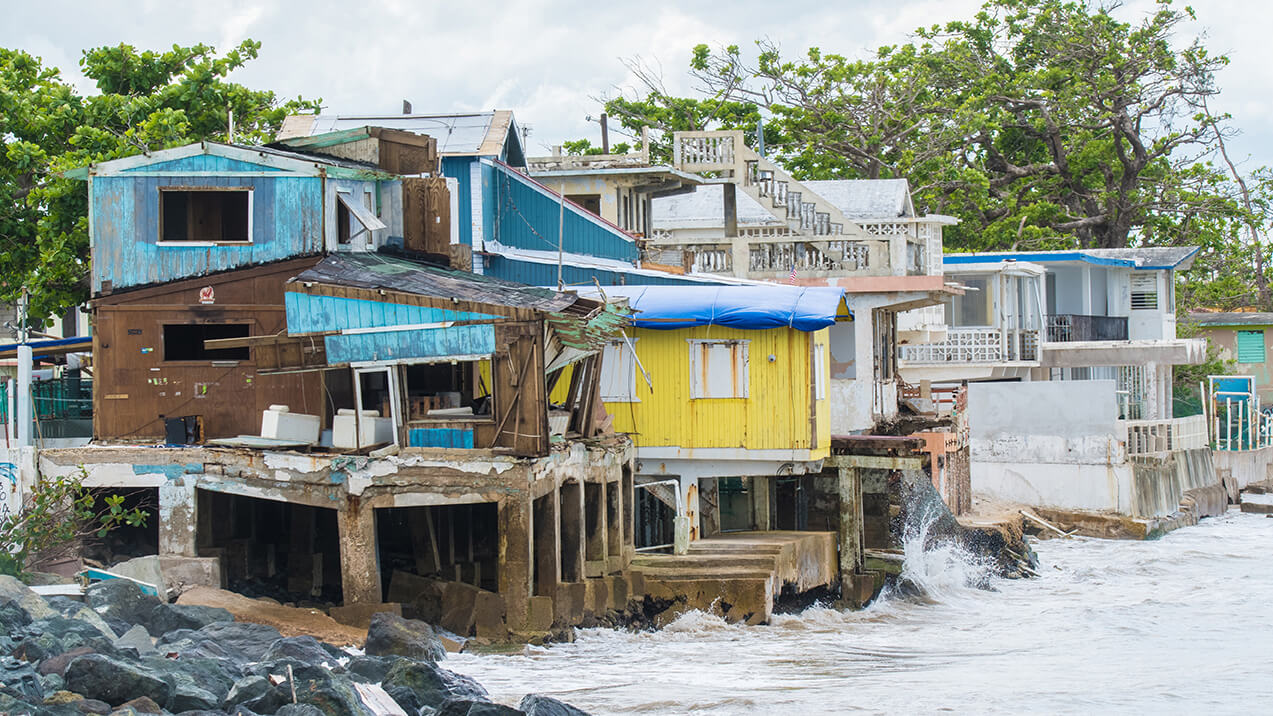

Puerto Rico’s location at the eastern edge of the Caribbean basin places it directly in the common path of storms moving from the Atlantic into the Caribbean Sea. This geographical positioning makes it one of the first significant landmasses that hurricanes encounter as they traverse westward from their points of origin. The warm waters of the Caribbean Sea act as fuel, potentially increasing the intensity of hurricanes as they approach the island.
Implications of a Changing Climate
Warmer ocean temperatures lead to more intense and potentially more frequent hurricanes while rising sea levels contribute to increased storm surge risks. These changing conditions require ongoing study to fully understand their implications for Puerto Rico and similar regions.
Technological Advances in Hurricane Tracking and Forecasting
Technological advancements have transformed the way hurricanes are tracked and forecasted. With the introduction of sophisticated tools and techniques, scientists and meteorologists are now able to predict the path and intensity of hurricanes with greater precision. Satellite imaging and computer modeling are at the forefront of these developments, providing crucial data that enhances the accuracy and timeliness of weather forecasts.
Satellite Imaging
Modern meteorology relies heavily on satellites to monitor weather patterns and track hurricanes as they develop. These satellites, equipped with advanced sensors, capture detailed images of the Earth’s atmosphere and surface. They can detect changes in temperature, humidity, and cloud formations, which are key indicators of hurricane activity. The imagery and data collected are used to monitor storm progress, intensity, and potential impact paths. This real-time information is vital for issuing timely warnings to potentially affected areas.
Computer Modeling
Alongside satellite technology, computer models are crucial in predicting hurricane paths and intensity. These models simulate the Earth’s atmosphere using equations that represent physical processes, such as air movement, temperature changes, and moisture interactions. By inputting data from satellite images and other meteorological sources, these models can project the future state of the atmosphere and predict where and when a hurricane will strike. Over the years, the accuracy of these models has improved dramatically, thanks to better data input and enhanced computational power.
Impact of Technology on Public Safety and Preparedness
Technological advancements have improved the accuracy of hurricane forecasts and extended the lead time for warnings. This enhanced forecasting allows for more effective evacuation strategies, reducing the risk of injury and death by providing residents more time. Additionally, the longer warning periods enable better protection of property, as individuals and businesses have more time to secure buildings against impending storms. Emergency management agencies also use these technologies to plan and effectively allocate disaster response and recovery resources.
Continued Innovation
The ongoing research and development in meteorological technology continue to push the boundaries of what is possible in weather forecasting. Innovations such as artificial intelligence and machine learning are being integrated into weather prediction models to enhance their accuracy further. As these technologies evolve, they promise even more reliable and precise forecasts, offering hope for improved management of hurricane impacts in Puerto Rico and other vulnerable regions around the world.
This kind of information is crucial for public safety and contributes to a broader understanding of how technology can be leveraged in disaster management and resilience building.
Nurturing Hope and Security
As we face the unpredictability of hurricane seasons, understanding the complexities and technological advancements in hurricane tracking and forecasting is crucial. These innovations in meteorology have significantly improved our ability to predict and prepare for hurricanes.
In Puerto Rico, where hurricanes are a part of life, the ability to effectively prepare for and respond to these natural disasters is important. In addition to the general strategies and technologies featured in this article, the effective implementation of disaster response and recovery programs is vital to aid with rebuilding efforts. Our work at Tidal Basin Caribe plays a crucial role in implementing these strategies and managing the recovery programs at a commonwealth and local level. Using emergency and disaster management best practices, our team at Tidal Basin Caribe helps communities across the Caribbean navigate the challenges of hurricanes more effectively.
To learn more about disaster preparedness strategies and how we help organizations and communities visit the Tidal Basin Caribe page.



