As the 14th named storm of the 2025 Atlantic hurricane season, Tropical Storm Nestor has reentered the spotlight, raising questions about its potential to develop into Hurricane Nestor. While the 2019 version of Nestor never reached hurricane status, it caused enough disruption to serve as a valuable case study in tropical storm preparedness.
In this article, we’ll explore the development and forecast of a potential 2025 Tropical Storm/Hurricane Nestor. We’ll also revisit the history of previous storms named Nestor and explore how tropical systems evolve, impact communities, and influence emergency response strategies.
What is Tropical Storm Nestor?
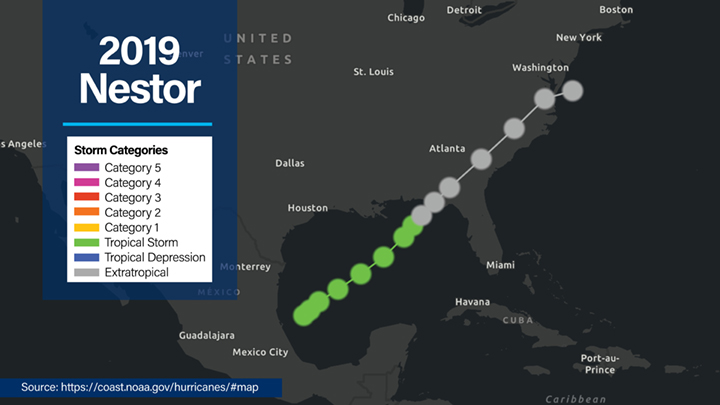
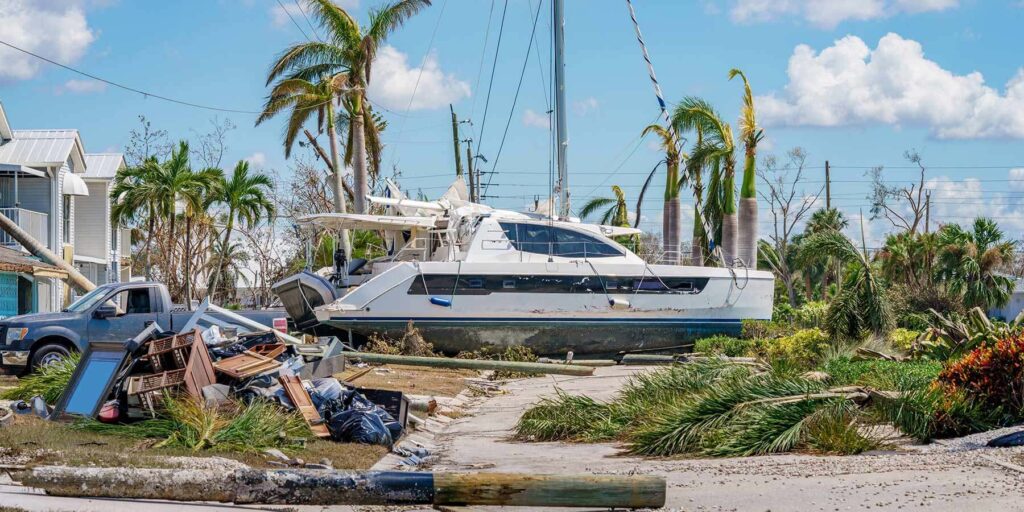
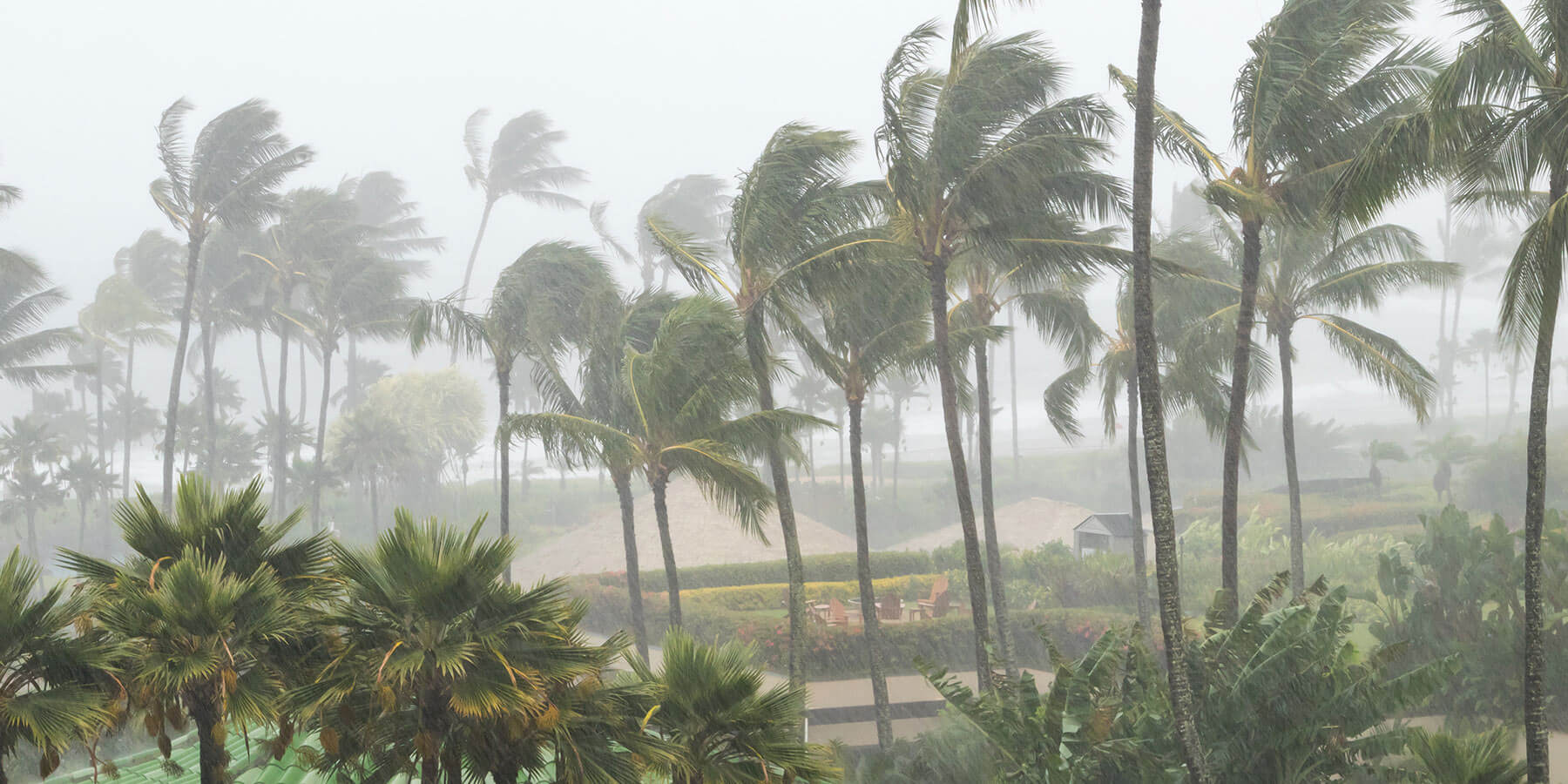
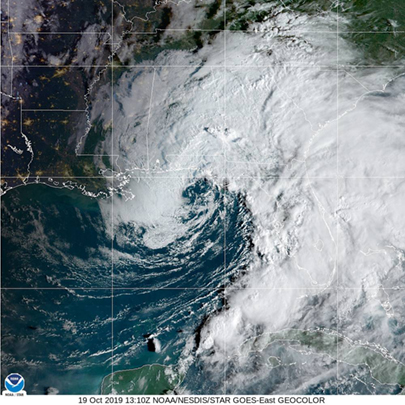
The first Tropical Storm Nestor formed in October 2019 in the Gulf. Despite it never reaching hurricane status, the storm still caused substantial disruption, affecting areas across the southeastern United States. It brought heavy rainfall, storm surges, and strong winds. It was a reminder that tropical storms, even without hurricane status, still demand serious attention and preparedness.
Why Tropical Storm Nestor Never Became a Hurricane
To classify a tropical storm as a hurricane, specific criteria must be met. A storm requires maximum sustained winds of at least 74 mph to achieve hurricane status. Nestor’s peak wind speeds reached 60 mph, falling short of this threshold.
While hurricanes tend to command greater attention due to their destructive capabilities, tropical storms like Nestor still bring hazardous conditions.
Impacts of Tropical Storm Nestor
Although Nestor did not escalate to hurricane-level intensity, its effects were far-reaching and significant.
Rainfall and Flooding
The storm brought widespread rainfall to areas of Florida and Georgia, leading to localized flooding. Low-lying regions experienced storm surges that disrupted transportation and damaged property.
Tornadoes
One of the most notable consequences of Tropical Storm Nestor was its influence in spawning tornadoes. Several tornadoes were reported, amplifying damage in heavily affected areas. Tornadoes associated with tropical storms often form rapidly, leaving limited time for authorities to warn or appropriately prepare residents.
Disruption to Communities
The storm’s broad footprint disrupted power systems, caused structural damage, and delayed day-to-day operations. The economic cost included property repairs and public infrastructure recovery efforts, proving how important it is to prepare for tropical storms.
Lessons Learned from Tropical Storm Nestor of 2019
Weather events like Tropical Storm Nestor emphasize the importance of proactive planning and preparation, regardless of a storm’s classification. Below are some key takeaways for emergency managers and government officials.
Don’t Underestimate Tropical Storms
Tropical storms are capable of causing extensive damage despite their classification. Relying solely on wind speed to gauge danger can be misleading. Rainfall, flooding, and tornadoes will lead to devastating outcomes if they’re not properly mitigated.
Keep Public Communication a Priority
Timely, accurate, and clear communication with the public is of paramount importance. Communities must be kept informed through various channels, including social media, news outlets, and public announcements. Clear instructions and updates can save lives.
Strengthen Interagency Collaboration
Effectively responding to storms requires collaboration between federal, state, and local agencies. Coordination between FEMA, local emergency responders, and infrastructure maintenance teams ensures that resources are efficiently distributed and recovery efforts are swift.
Invest in Technology and Training
Using predictive models and early warning systems based on real-time weather data can significantly improve preparation efforts. For example, adopting tools that incorporate artificial intelligence can offer better storm tracking and impact forecasts. Additionally, regular training simulations for emergency response teams can enhance their readiness for future weather events.
Differences Between Tropical Storms and Hurricanes
For a clearer understanding of Tropical Storm Nestor and similar systems, it’s helpful to examine their differences from hurricanes. The table below outlines some of the key distinctions between the two classifications.
| Feature | Tropical Storm | Hurricane |
|---|---|---|
| Wind Speed | 39-73 mph (34-63 knots) | 74 mph (64 knots) or higher |
| Damage Potential | Moderate; can cause localized flooding and wind damage | Severe; capable of widespread destruction, including structural damage and major flooding |
| Structure | Less organized, with no clearly defined center | Well-organized, symmetric structure with a defined eye at the center |
| Tornadic Activity | Possible, though less frequent | More likely, particularly in the outer rainbands, due to increased atmospheric instability |
Formation of Hurricane Nestor
Hurricane Nestor, like other tropical cyclones, may originate from a combination of favorable atmospheric and oceanic conditions. These include warm sea surface temperatures of at least 80°F (27°C), which provide the necessary heat and moisture to fuel the storm. Low vertical wind shear is also essential, as strong wind shear can disrupt the development and organization of the storm’s structure. The process typically begins with a cluster of thunderstorms over tropical or subtropical waters, known as a tropical disturbance.
If the disturbance encounters the right environmental conditions, it can develop into a tropical depression, with organized circulation and sustained wind speeds below 39 mph (34 knots). Continued strengthening will lead to a tropical storm and, eventually, a hurricane when sustained winds exceed 74 mph (64 knots). The Coriolis effect, caused by Earth’s rotation, helps initiate and maintain the storm’s spin. If these elements align and persist, Hurricane Nestor could form, following a complex yet predictable sequence of atmospheric dynamics.
Hurricane Nestor, like all hurricanes, is classified into five categories based on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale. This scale measures the intensity of the storm’s sustained wind speeds, ranging from Category 1, with winds between 74-95 mph (64–82 knots), to Category 5, which features devastating winds exceeding 157 mph (137 knots).
Each category reflects the potential level of damage the hurricane could inflict on property, infrastructure, and natural landscapes. Beyond wind intensity, other destructive elements include storm surges, heavy rainfall, and flooding, which can extend the impact far beyond the hurricane’s immediate path.
Frequently Asked Questions About Tropical Storm Nestor/Hurricane Nestor
How can governments improve preparation for storms like Nestor?
Governments can utilize advanced weather prediction tools, train emergency responders, invest in resilient infrastructure, and maintain clear public communication strategies.
What areas were most affected by Tropical Storm Nestor in 2019?
The Tropical Storm Nestor of 2019 primarily impacted parts of the southeastern United States, bringing heavy rain, flooding, and isolated tornadoes to the region.
How do meteorologists name tropical storms?
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) maintains a list of names for tropical storms, rotating every six years. Names are retired if the storm was particularly deadly or costly.
What steps should individuals take to prepare for a tropical storm?
Individuals should stock up on emergency supplies, create an evacuation plan, secure their property, and stay informed through reliable weather update services like the National Weather Service (NWS).
Can tropical storms turn into hurricanes?
Yes, tropical storms can strengthen into hurricanes if they gain enough energy, typically from warm ocean waters and favorable atmospheric conditions.
What is the difference between a tropical storm watch and a warning?
A watch means conditions are possible within 48 hours, while a warning means conditions are expected within 36 hours.
How long did Tropical Storm Nestor 2019 last?
Tropical Storm Nestor formed on October 17, 2019, and transitioned to a post-tropical cyclone by October 19, 2019. It remained a named tropical system for approximately two days before losing its tropical characteristics.
Looking Ahead This Hurricane Season
Tropical Storm Nestor is a clear reminder that even lower-category systems can disrupt communities, damage infrastructure, and strain emergency resources. It didn’t reach hurricane status, but it still delivered flooding, tornadoes, and power outages across the Southeast. Preparedness and response strategies can’t rely on storm category alone, they need to account for the full range of impacts.
If your community needs support in planning, responding to, or recovering during this hurricane season, get in touch today. Our team brings deep experience to help you act early, respond fast, and recover stronger.